Customers today have become very conscious of pricing. Pricing can affect how consumers perceive brands, make purchasing decisions, and develop loyalty. What that means for brands is that with numerous retailers and online sellers vying for customer attention, maintaining consistent pricing across platforms is critical to brand integrity and profitability. This includes issues like MAP violations, seller performance, and managing products across marketplaces.
MAP (Minimum Advertised Price) policies help prevent price violations and establish a level playing field among sellers. They are crucial in reducing MAP violations that can undermine pricing strategies, erode customer trust, and damage a brand’s reputation.
Let’s explore what MAP violations are, why they matter, and the various tools and techniques available to help brands detect and stop them. Whether you’re a brand looking to enforce MAP policies or a retailer hoping to understand the rules better, this guide will provide actionable insights into how to maintain compliance and minimize the impact of MAP violations on your business.
What is the Minimum Advertised Price (MAP)?

Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) refers to the lowest price at which a brand allows its retailers or distributors to advertise a product for sale.
It’s important to note that MAP policies regulate advertised prices, not actual sale prices. Retailers are still free to sell products at any price they choose, but they cannot publicly advertise prices lower than the MAP set by the brand.
How MAP Policies Work?
MAP policies serve as a crucial framework for brands to control the prices at which their products are advertised across various platforms. These policies are not about dictating the final selling price to consumers but are focused on the advertised price that retailers use to promote the product.
This distinction allows for flexibility in actual sales pricing while ensuring a uniform product pricing strategy that protects brand equity and market positioning.
MAP policies are designed to:
1. Maintain brand value by preventing price wars
Price wars can quickly erode the perceived value of a brand. When retailers begin competing solely on price, it often leads to a race to the bottom. In these scenarios, retailers cut their margins to undercut competitors, which can be especially detrimental to premium brands.
A product that is frequently discounted or advertised at below-market rates starts to lose its prestige and value in the eyes of consumers. This can not only affect immediate sales but also have long-term consequences on the brand’s reputation.
2. Ensure fair competition among sellers
The retail environment, especially in e-commerce, is highly competitive. Large retailers with vast resources may attempt to use their size and scale to dominate the market by offering significant discounts that smaller retailers cannot match.
This can lead to an uneven playing field where smaller or niche sellers are squeezed out, which diminishes the diversity of retail options for consumers.
MAP policies level the playing field by ensuring that all retailers—large or small—adhere to the same minimum advertised price for a given product. This allows retailers to compete on factors other than price, such as customer service, shipping speed, and additional services, rather than engaging in price wars.
3. Protect smaller retailers from being undercut by large retailers
In the absence of MAP policies, smaller retailers often find themselves at a disadvantage when competing with large retail chains or major e-commerce platforms like Amazon.
These larger players have more bargaining power and can afford to sell products at a loss to attract customers—a strategy known as “loss-leader pricing.” For small retailers, this kind of pricing pressure is unsustainable, leading them to either exit the market or be driven out of business.
MAP policies serve to protect these smaller retailers by ensuring that larger retailers cannot advertise products below a certain threshold. This helps maintain healthy competition and gives smaller players a fighting chance to compete in the market without being completely overwhelmed by discount-driven strategies from bigger competitors.
Importance of MAP Policies in Retail and E-commerce
The significance of MAP policies extends beyond just price regulation; they are a critical component of maintaining a well-balanced retail ecosystem.
As the retail landscape continues to shift more towards digital platforms and global e-commerce, the role of MAP policies becomes even more crucial.
Here’s why:
- Preserving Brand Integrity and Perception
- Ensuring Profitability for Retailers
- Preventing “Showrooming” and the Devaluation of Brick-and-Mortar Stores
- Creating a Consistent Brand Experience Across Channels
- Managing Price Parity Across Global Markets
- Protecting Against “Gray Market” Sales
- Maintaining Retailer Relationships
- Addressing the Challenges of E-commerce
Understanding MAP Violations? and How to Identify Them?
What Constitutes a MAP Violation?
MAP violations occur whenever a product is advertised at a price lower than the set minimum. This can happen across a variety of platforms, including:
- Online marketplaces (e.g., Amazon, eBay)
- Retailer websites
- Social media promotions
- Print ads
- Email campaigns
While some MAP violations are deliberate, others may result from confusion over the policy or technological errors. Regardless of intent, these violations disrupt the competitive environment and can have wide-reaching impacts on brand value.
Common Examples of MAP Violations

Some examples of MAP violations include:
- Online price listings below MAP: A retailer lists a product on their website for less than the agreed MAP.
- Coupon code abuse: A retailer offers a discount that brings the advertised price below MAP when a coupon is applied.
- Email marketing violations: Sending email promotions that advertise prices below the MAP threshold.
- “In Cart” pricing: Displaying the MAP price on the product page, but reducing the price once the product is added to the shopping cart.
- Marketplace violations: Offering products below MAP on third-party platforms like Amazon, eBay, or Walmart.
How do MAP Violations Affect E-Commerce Brands and Retailers?
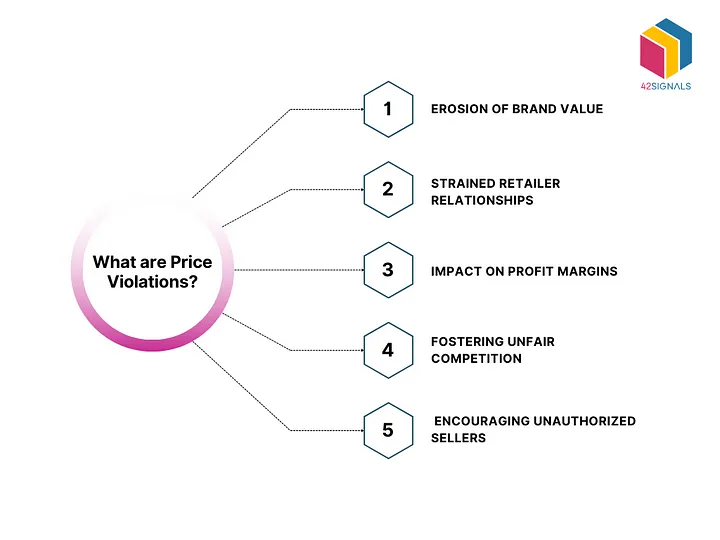
MAP violations can have several negative effects on both brands and retailers:
- Erosion of brand value: When a brand’s products are consistently advertised below MAP, it can lead to a perception that the brand’s value has diminished.
- Loss of retailer trust: Retailers who follow MAP policies can become frustrated when they see competitors undercutting them without consequence, leading to strained relationships with the brand.
- Downward pricing pressure: MAP violations can spark price wars, driving prices lower and forcing other retailers to follow suit, even if it harms profitability.
- Impact on pricing strategies: Brands that rely on premium pricing models may struggle to maintain those models when MAP violations occur frequently, forcing them to re-evaluate their pricing strategies.
How MAP Violations Affect Pricing Strategies
MAP violations have a profound impact on a brand’s pricing strategy, and they can ripple through a company’s entire pricing structure, affecting profitability, market positioning, and customer perception.
When retailers advertise products below the Minimum Advertised Price (MAP), it not only disrupts a brand’s ability to maintain consistent pricing but also creates a chain reaction that influences other pricing decisions within the market.
For example, if a product consistently appears at a price lower than the MAP, consumers may begin to question the quality or prestige associated with that product. A luxury or premium brand, in particular, relies on higher pricing to communicate exclusivity and quality.
Frequent MAP violations can erode this perception, leading to a diluted brand image.
Another example would be if a product is advertised below MAP on an online marketplace but is sold at full price in physical stores, it creates a disjointed customer experience. Shoppers who are savvy enough to compare prices across channels will gravitate towards the lower-priced option, leaving other sales channels underperforming.
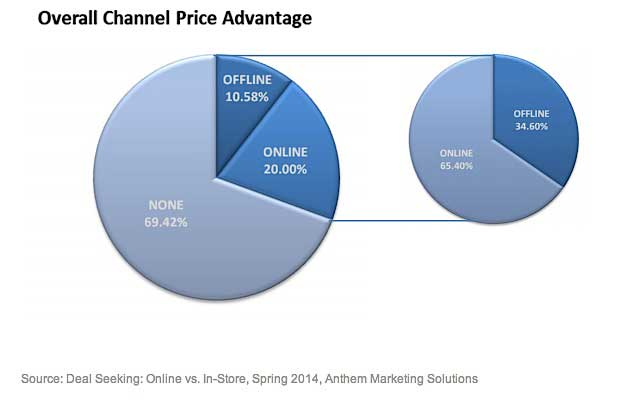
Image Source: Marketing Profs
This disparity can also harm relationships with compliant retailers, who may feel unfairly disadvantaged when their competitors are allowed to undercut them due to MAP violations.
Looking at discounts, a brand may decide to offer a limited-time 10% discount on a specific product across all authorized retailers. However, if some retailers have already violated MAP and advertised the product at a 20% discount, the brand’s promotion becomes redundant.
Customers are less likely to respond to the new promotion, as they have already seen lower prices elsewhere.
How to Identify and Prevent MAP Violations in E-Commerce?
Monitoring for MAP violations can be a daunting task, especially for brands with large retailer networks or those operating in multiple regions. Brands must be vigilant in tracking advertised prices across various platforms to ensure that MAP compliance is being maintained.
Top Tools for Detecting MAP Violations
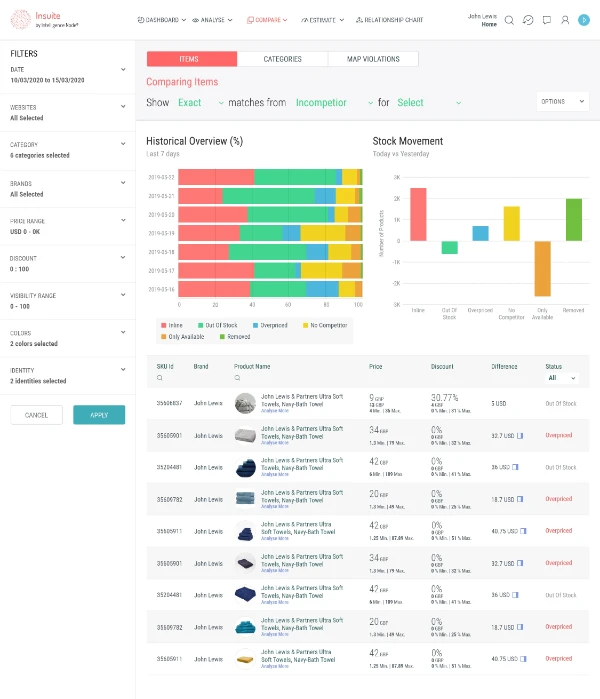
Image Source: Dealavo
Several tools and services are available to help brands detect and identify MAP violations. These include:
- Price monitoring software: These tools continuously track pricing across multiple channels and platforms to detect instances where products are advertised below the MAP.
- Marketplace monitoring tools: Specific to platforms like Amazon or eBay, these tools identify MAP violations in real time and alert brands to potential issues.
- Manual checks: For smaller brands, manual monitoring of retail partners can be an effective, though time-consuming, way to ensure compliance.
Identifying MAP Violation Patterns
Tracking patterns in MAP violations can help brands identify problem areas and chronic violators.
Common patterns include:
- Frequent violators: Some retailers may consistently advertise products below MAP, often relying on limited enforcement by the brand.
- Time-specific violations: Violations may increase during certain sales periods, such as Black Friday, Cyber Monday, or holiday sales.
- Platform-specific violations: MAP violations are often more common on certain platforms, such as Amazon or eBay, where price competition is fierce
How to Search for Competitor MAP Violations
Brands should also monitor competitors to ensure they are adhering to MAP policies. This can be done by:
- Monitoring pricing on major marketplaces.
- Tracking competitor email campaigns and promotional materials.
- Utilizing price monitoring tools to compare across multiple sellers.
Common Indicators of MAP Violators
Some red flags indicating potential MAP violations include:
- Significant price drops during promotions.
- Discounts that are not clearly aligned with brand-wide promotions.
- “Hidden” prices that only appear at checkout or in email campaigns.
How to Enforce MAP Policies and Prevent Price Violations?
Effective enforcement of MAP policies is essential to maintaining compliance and ensuring fair competition. When a MAP violation is detected, brands should take a systematic approach to enforcement.
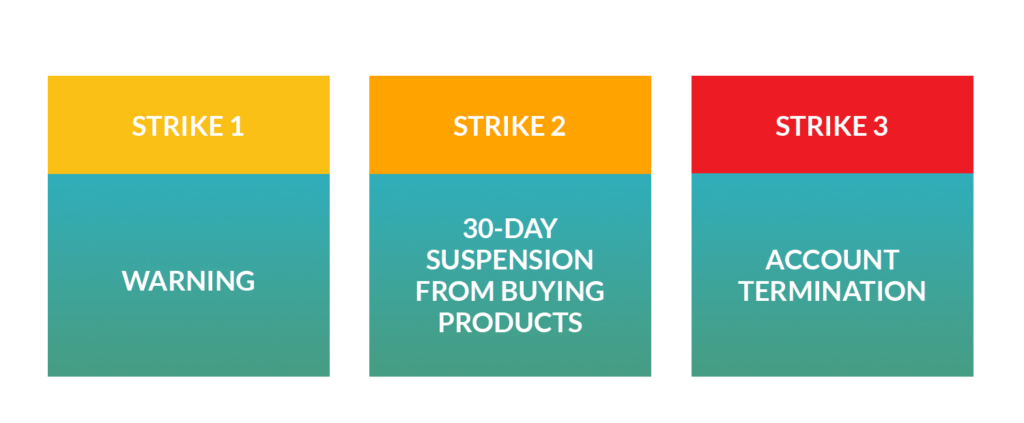
Steps for Effective MAP Policy Enforcement
- Document the violation: Gather evidence, such as screenshots, of the pricing discrepancy.
- Notify the violator: Send a formal notice to the retailer, outlining the specific violation and the steps required to remedy it.
- Escalate the issue: If the violation is not addressed, consider issuing warnings or imposing penalties, such as reducing stock availability or terminating the retailer agreement.
- Regular monitoring: Continuous monitoring is crucial to ensure that violators do not resume the practice after initial enforcement.
Legal Considerations in Enforcing MAP Policies
Enforcing MAP policies can raise several legal concerns. Brands must ensure that they are acting within the bounds of antitrust and competition laws, as improper enforcement could expose them to legal risks.
MAP policies fall into a complex area of law that touches on antitrust, competition, and fair trade practices. Improper enforcement of MAP policies can expose brands to significant legal risks, such as accusations of price-fixing or anti-competitive behavior.
- Vertical price fixing: MAP policies should not be used to dictate the actual sale price of products, as this could be considered illegal price fixing.
Vertical price fixing occurs when a manufacturer or supplier directly controls the final sale price of a product, rather than allowing retailers to determine the actual price at which the product is sold.
This kind of price manipulation can reduce competition, leading to higher prices for consumers, and is therefore prohibited by various legal frameworks in many regions, including the United States under the Sherman Antitrust Act and similar laws.
- Regional differences: MAP enforcement can vary across jurisdictions, so brands should be mindful of local laws governing price setting and enforcement.
What is considered legal in one country might be viewed as anti-competitive or illegal in another. For example, while MAP policies are generally allowed in the United States, they are subject to scrutiny under European Union competition law.
In the EU, strict price controls—such as dictating retail prices through MAP policies—may be seen as price fixing, which violates Article 101 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU).
Similarly, in countries like Canada and Australia, MAP policies may be viewed unfavorably if they are perceived as limiting competition or harming consumers.
Some regions have stricter rules regarding how much control manufacturers can exert over retail pricing, and brands that operate in global markets must adapt their MAP enforcement strategies accordingly.
- Antitrust and competition law compliance: MAP policies, if not managed properly, can give rise to antitrust concerns, particularly if a brand is seen as limiting competition.

Image Source: YouTube
The key to ensuring compliance is demonstrating that the policy is in place to protect brand integrity and market fairness, rather than stifling competition.
Antitrust regulators may scrutinize MAP policies, especially if they believe that the enforcement is too aggressive or used in conjunction with other price-control mechanisms.
How to Manage Non-Compliant Sellers and Enforce MAP Policies?
Enforcing MAP policies is an ongoing challenge, and dealing with sellers who consistently violate these policies requires a well-thought-out approach. Brands must balance the need to protect their pricing integrity with maintaining strong relationships with their retail partners.
For sellers that consistently violate MAP policies, brands may consider:
- Cutting off supply: For retailers that continuously disregard MAP policies despite repeated warnings, cutting off their supply may be the most effective measure. Terminating the business relationship signals to both the violating retailer and other sellers that the brand is serious about enforcing MAP compliance.
It also removes the offending party from the retail ecosystem, preventing them from further damaging the brand’s pricing integrity.
However, cutting off supply should be seen as a last resort. Brands should ensure they have documented all violations, given fair warning, and provided ample opportunity for the retailer to correct their behavior before taking this step.
- Public warnings: In some cases, brands may choose to publicly name violators as a deterrent to others.
Publicly calling out a violator can harm their reputation within the industry and among consumers, potentially causing them to reconsider their approach to MAP compliance. This tactic is often used when private warnings have failed to produce results.
However, this approach should be used with caution. Public warnings can damage relationships and might backfire if the retailer decides to retaliate by further undercutting prices or damaging the brand’s reputation in return.
Additionally, public shaming can draw unwanted attention to pricing disputes, potentially leading to regulatory scrutiny if there are concerns about anti-competitive practices.
- Tiered pricing: Rather than using punitive measures, some brands incentivize compliance by offering tiered pricing to retailers who consistently adhere to MAP policies.
This strategy rewards compliant sellers with more favorable pricing or additional benefits, such as better terms, exclusive access to new products, or higher inventory allocations. By offering these incentives, brands encourage retailers to follow MAP policies voluntarily, as non-compliant sellers are excluded from these benefits.
Tiered pricing not only strengthens relationships with compliant retailers but also allows brands to maintain a more cooperative approach to MAP enforcement.
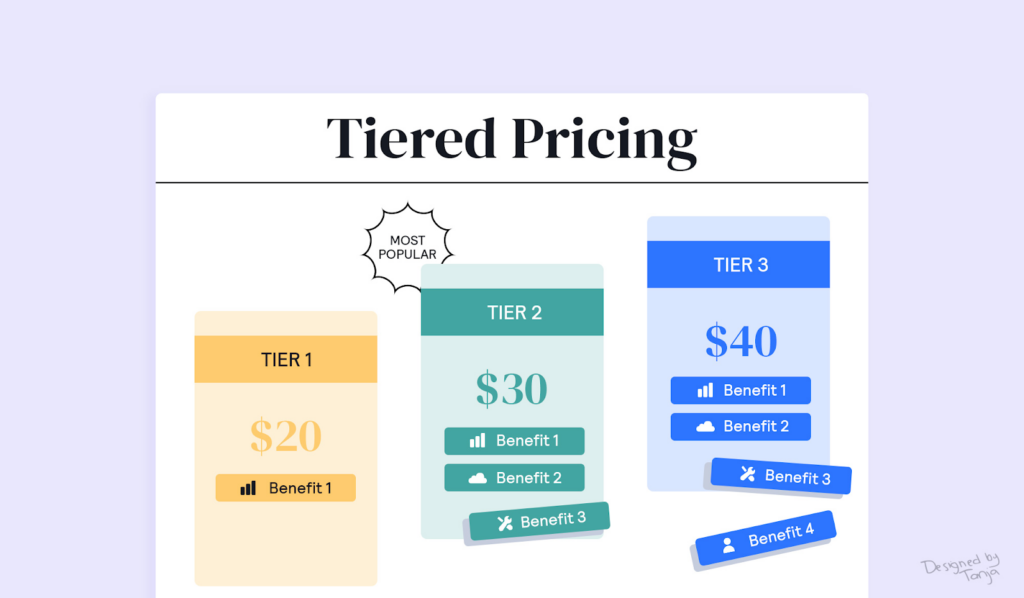
Image Source: Better Proposals
It creates a positive reinforcement model where retailers are motivated to follow the rules in order to reap the rewards, reducing the likelihood of MAP violations in the future.
How MAP Compliance Tools Help in Enforcing MAP Policies Effectively?
MAP compliance tools play an essential role in automating the enforcement process. As the retail landscape becomes increasingly complex, with numerous online channels and third-party marketplaces, manual monitoring for MAP violations becomes nearly impossible.
These tools use advanced technologies, such as web crawlers, AI, and machine learning algorithms, to monitor a vast array of platforms, making it easier to identify violations. It can help brands:
- Track pricing across multiple channels
One of the biggest challenges in enforcing MAP policies is the sheer volume of platforms that need to be monitored, including retailer websites, e-commerce platforms (such as Amazon, eBay, and Walmart), social media, and digital marketplaces. MAP compliance tools continuously track pricing across these channels, ensuring that no retailer or platform is overlooked.

These tools can monitor thousands of listings simultaneously, capturing advertised prices across diverse geographical locations, languages, and currencies. This comprehensive monitoring provides brands with a clear, real-time view of how their products are being advertised, ensuring they can act quickly when violations are detected.
By automating this process, MAP compliance tools eliminate the need for manual checks, freeing up time for brand managers to focus on strategic initiatives rather than price monitoring.
- Send automatic notifications to violators
Once a MAP violation is detected, swift action is essential to minimize the impact on brand value and pricing strategies. MAP compliance tools allow brands to automatically send notifications to retailers when they breach the MAP agreement.
These notifications can be customized to specify the violation, provide evidence (such as screenshots), and outline the steps the retailer needs to take to rectify the issue.
By automating this notification process, brands can address violations almost immediately, preventing prolonged instances of undercutting that could damage relationships with other retailers.
The automatic generation of notifications ensures consistency and impartiality in enforcement, reinforcing the importance of compliance without the need for direct intervention from the brand’s legal or compliance teams.
These tools also allow brands to set up tiered responses, meaning that retailers can receive an escalating series of warnings if they do not comply after the initial notification.
For instance, the first violation might trigger a friendly reminder, while repeated violations could result in more serious consequences, such as supply cuts or legal action.
- Provide real-time alerts when MAP violations occur
Time is of the essence when it comes to MAP enforcement. The longer a MAP violation remains unaddressed, the greater the potential damage to the brand’s pricing integrity and relationships with compliant retailers.
MAP compliance tools provide real-time alerts, allowing brands to act the moment a violation is detected.
These real-time alerts are sent via email, dashboards, or mobile notifications, enabling brands to stay on top of pricing violations regardless of where they occur. Real-time insights also allow for immediate action to prevent a violation from spreading across multiple channels.
For example, if one retailer starts undercutting prices on a major platform, others may follow suit quickly. By catching the violation early, brands can halt the ripple effect and maintain pricing consistency across all channels.
- Tracking Historical Pricing Data and Violation Patterns
MAP compliance tools not only monitor current prices but also track historical pricing data. This allows brands to analyze trends and identify patterns of non-compliance over time.
By maintaining a comprehensive database of past violations, brands can determine which retailers are chronic offenders and assess how pricing behaviors fluctuate during specific periods, such as holiday sales or promotional events.
This historical data is invaluable for making informed enforcement decisions. For example, if a retailer consistently violates MAP policies during certain times of the year, the brand can anticipate these behaviors and implement pre-emptive measures to prevent future violations.
Additionally, historical data helps brands identify problematic platforms or regions where MAP violations are more prevalent, allowing for more focused and effective enforcement efforts.
MAP Violations on Different E-Commerce Platforms
1. Amazon MAP Violations
Amazon is one of the largest and most complex marketplaces when it comes to MAP enforcement. Given its scale and the number of third-party sellers, it is difficult for brands to maintain consistent pricing. Unauthorized sellers and price undercutting are rampant, making MAP violations on Amazon a significant issue.
Overview of Amazon’s MAP Policies
Amazon itself does not enforce MAP policies on behalf of brands. Instead, it provides tools through its Brand Registry program that allow brands to monitor and report MAP violations. Amazon prioritizes providing consumers with the best possible price, so it is up to the brand to enforce MAP compliance.
Common Amazon MAP Violations include…
- Third-party sellers offering products below MAP.
- “In Cart” pricing that lowers the advertised price below MAP thresholds.
- Unauthorized sellers list the product without following MAP policies.
Since Amazon operates on a global scale, enforcing MAP policies across different regions and sellers can be particularly challenging.
Strategies to Address Amazon MAP Violations
To address MAP violations on Amazon, brands can:
- Enroll in Amazon’s Brand Registry to gain greater control over product listings.
- Use third-party MAP monitoring tools to track violations in real time.
- Work with Amazon MAP violation attorneys to navigate legal complexities and take action against chronic violators.
- Submit formal reports to Amazon against unauthorized sellers or violators.
Here are a few other stories on how big brands like HP and Boehringer Ingelheim combated MAP Violations.
2. HP MAP Violations
Hewlett-Packard (HP) is another brand that has faced challenges with MAP violations, particularly in the tech and electronics sector. HP has implemented strict MAP policies to maintain its product’s premium status, but frequent violations occur, especially on online marketplaces.
HP uses a combination of monitoring tools and legal enforcement to address these issues, but challenges persist due to the volume of sellers involved.
3. Boehringer Ingelheim MAP Violations
Boehringer Ingelheim, a pharmaceutical company, has also struggled with MAP enforcement in the health and wellness sector. Due to the nature of the pharmaceutical and health product industry, maintaining consistent pricing is crucial for ensuring product trust and integrity.
However, widespread violations on online platforms and through third-party sellers have prompted the company to implement stricter compliance and enforcement measures.
Strategies to Prevent MAP Violations and Protect Your Pricing
Preventing MAP violations begins with clear communication and proactive monitoring. Brands should establish comprehensive MAP policies that are easy to understand and enforce.
Additionally, investing in robust compliance tools and conducting regular audits are essential for identifying potential issues before they escalate.
A few key strategies include:
- Educating retailers about MAP policies.
- Utilizing price monitoring tools.
- Setting up tiered enforcement protocols to ensure timely responses.
Proven Strategies to Prevent MAP Violations
Maintaining Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) compliance is crucial for protecting a brand’s pricing strategy, maintaining market integrity, and ensuring fair competition among retailers. However, MAP enforcement can be challenging, especially when dealing with numerous sales channels, including e-commerce platforms and third-party marketplaces.
Below are expanded best practices for maintaining MAP compliance:
1. Consistent Communication with Retailers
The foundation of successful MAP compliance lies in clear, open, and ongoing communication between brands and retailers. Ensuring that all retail partners understand the importance of MAP policies and their role in maintaining market stability is crucial for long-term compliance.
- Initial Policy Communication: From the outset of the relationship, brands should provide a detailed overview of their MAP policies during the onboarding process with each new retailer.
- Regular Updates and Reminders: As MAP policies evolve or when there are changes in the market, it’s essential to keep all retailers informed. Regular updates should be communicated through multiple channels, such as email newsletters, webinars, or meetings, to ensure that retailers stay up-to-date on any revisions.
- Dedicated Support Channels: Brands should offer retailers a dedicated support channel where they can ask questions or seek clarifications regarding MAP policies. This can be in the form of a MAP compliance hotline, email support, or an online portal where retailers can access policy documents and FAQs.
- Partnership Collaboration: MAP enforcement should not be seen as a punitive measure. Instead, brands can work collaboratively with their retail partners to foster a shared commitment to maintaining fair pricing.
2. Automating Price Monitoring

One of the most effective ways to maintain MAP compliance is through automated price monitoring. Given the scale and complexity of modern retail, particularly in e-commerce, manual monitoring is inefficient and prone to errors. Automating the process ensures continuous oversight and enables brands to enforce MAP policies in real-time.
- Real-Time Monitoring Across Platforms: Automated price monitoring tools track prices across a wide range of platforms, including retailer websites, third-party marketplaces like Amazon and eBay, and international online stores.
- Comprehensive Data Collection: By collecting historical pricing data, automated tools can help brands identify trends and patterns in MAP violations. This allows brands to pinpoint problematic retailers or periods when violations are more likely to occur (e.g., during sales events or holidays), enabling proactive intervention.
- Automatic Violation Notifications: Once a MAP violation is detected, automated systems can send alerts to the brand and the retailer involved. These alerts often include a snapshot of the violation, providing clear evidence that can be addressed immediately. Automated notifications reduce response times and enable brands to enforce policies more efficiently.
- Scalability: For brands with a large network of retailers, manual monitoring is simply not scalable. Automated tools allow brands to manage MAP compliance across hundreds or thousands of retail partners without dedicating significant manpower to the task.
- Third-Party Marketplace Monitoring: Automated tools can also help monitor third-party sellers who frequently violate MAP policies on platforms like Amazon. Many of these sellers operate independently of authorized retailers, making it difficult for brands to maintain pricing consistency without automation.
3. Providing Incentives for Compliance
While punitive actions for MAP violations (such as cutting off supply or imposing penalties) are necessary for non-compliant retailers, brands can also encourage adherence to MAP policies through positive reinforcement. Providing incentives for compliance helps foster goodwill and motivates retailers to stick to MAP guidelines.
- Preferred Pricing and Terms: Brands can offer compliant retailers more favorable pricing terms, such as early access to product launches, exclusive distribution rights, or higher-margin products.
- Priority Inventory Allocation: During peak seasons or product shortages, brands can allocate inventory preferentially to retailers that consistently follow MAP policies.
- Exclusive Promotions and Marketing Support: Offering compliant retailers access to exclusive promotional events, co-marketing opportunities, or higher visibility in brand-sponsored campaigns can serve as an incentive to maintain MAP adherence.
- Tiered Reward Systems: Brands can implement a tiered reward system where the most compliant retailers receive additional benefits based on their adherence to MAP policies.
For example, those who have zero MAP violations over a specific period might gain access to premium marketing materials, while those with minor violations could receive lesser rewards. This creates a positive reinforcement loop, where retailers actively work toward maintaining compliance to earn benefits.
4. Developing Clear, Enforceable Contracts
A critical component of MAP compliance is ensuring that MAP policies are embedded within legally binding retailer contracts. Every retail agreement should clearly outline the expectations around MAP adherence, the processes for addressing violations, and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
- Including Specific Terms and Definitions: Contracts should specify the exact terms of MAP compliance, such as what constitutes an advertised price versus a final sales price, how promotions and discounts are to be handled, and the scope of the agreement (e.g., does it apply to all regions or only specific channels?).
- Outlining Violation Procedures: Retailer contracts should include explicit procedures for how MAP violations will be addressed, including the notice period, penalties, and any potential grace periods for correction. This ensures that all parties are aware of the consequences and are prepared to respond appropriately if a violation occurs.
- Ensuring Flexibility for Promotions: While enforcing MAP policies is critical, it’s equally important to allow some flexibility for legitimate promotional activities. Contracts should outline scenarios where retailers can offer discounts without violating MAP, such as limited-time brand-sponsored sales or coupons that comply with MAP rules.
- Regular Reviews and Revisions: As markets evolve, so too should MAP policies. Brands should regularly review and update their retailer agreements to ensure that MAP policies remain relevant and enforceable. Revising contracts based on feedback from retailers and changing market conditions can help ensure that all parties remain aligned on the best practices for maintaining MAP compliance.
Tools and Services to Help Prevent MAP Violations
Preventing Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) violations is essential for brands seeking to maintain pricing consistency, protect brand value, and ensure fair competition across retailers. To achieve this, brands can leverage various tools and services designed to streamline MAP monitoring, detect violations early, and enforce compliance across multiple sales channels.
These solutions allow brands to take a proactive approach to preventing MAP violations, ensuring that their products are advertised at consistent prices regardless of the platform or seller.
Below is a breakdown of key tools and services that assist in preventing MAP violations, including an introduction to 42Signals, a cutting-edge MAP monitoring platform:
1. Price Monitoring Software
One of the most effective ways to prevent MAP violations is through the use of price monitoring software. These tools continuously scan websites, marketplaces, and other online platforms to identify pricing discrepancies.
Automated price monitoring software reduces the need for manual checks, providing an efficient way for brands to track compliance across hundreds, or even thousands, of retailers.
Key features of price monitoring software include:
- Real-Time Monitoring
- Automated Alerts
- Data Collection and Reporting
2. Enforcement Services
Even with effective monitoring, enforcement is a critical step in maintaining MAP compliance. Legal enforcement services can assist brands in addressing violations, particularly when retailers or third-party sellers refuse to comply with MAP policies.
These services provide the expertise needed to navigate the complex legal landscape surrounding MAP policies and ensure that enforcement actions are carried out in a compliant and effective manner.
- Legal Advice and Consultation
- Formal Violation Notices
- Litigation Support
3. Marketplace Monitoring Tools
Marketplace monitoring tools are specifically designed to help brands manage MAP compliance across e-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, Walmart, and other third-party sites. These tools offer a more targeted approach to tracking and enforcing MAP policies on marketplaces that often feature numerous sellers, many of whom may not be officially authorized.
- Third-Party Seller Tracking
- Automated Violation Detection
- Seller Reporting and Take-Down Assistance
42Signals – Helps Brands with MAP Monitoring and Enforcement
One powerful tool in the arsenal for preventing MAP violations is 42Signals, a comprehensive price monitoring and marketplace tracking solution.
Designed to address the specific challenges of MAP compliance, 42Signals provides brands with the technology to detect violations early, take action swiftly, and maintain a consistent pricing strategy across all platforms.
Here are some key features of 42Signals,
- Real-Time Price Monitoring 42Signals offers real-time price monitoring across a vast array of websites, marketplaces, and retail platforms. With its powerful web-crawling capabilities, 42Signals scans prices across all relevant sales channels, alerting brands the moment a MAP violation occurs. This enables quick corrective actions and minimizes the duration and impact of violations.
- Automated Violation Alerts The platform sends automated alerts to brands when it detects MAP violations. These alerts can be configured to suit the brand’s specific needs, ensuring that the brand is notified immediately, either via email or in-platform dashboards, when a product is advertised below the MAP. This helps prevent prolonged pricing discrepancies that could lead to market instability.
- Detailed Reports and Analytics 42Signals provides brands with a wealth of data, including detailed reports on pricing trends, historical violations, and repeat offenders. This allows brands to track patterns in MAP violations, making it easier to enforce policies and identify which retailers or marketplaces are most prone to undercutting prices. The platform also provides insights into pricing behaviors during key sales periods, such as holidays or promotional events.
- Multi-Channel Monitoring Whether it’s a traditional e-commerce website, a major marketplace like Amazon, or an international platform, 42Signals can monitor pricing across multiple channels. This ensures that brands maintain a consistent MAP enforcement strategy, even across borders and various sales regions.
- Advanced Seller Identification One of the most challenging aspects of MAP enforcement on marketplaces is identifying unauthorized or rogue sellers. 42Signals helps brands track third-party sellers, identifying those who may not be authorized to sell the product and reporting them directly to the platform for removal. This helps eliminate gray market listings, protecting the brand’s pricing strategy and preventing MAP violations.
- Customizable Dashboards The platform offers customizable dashboards, allowing brands to view MAP compliance data in a way that suits their business needs. Brands can track violations by region, seller, or platform, providing granular insights that enable a targeted enforcement strategy.
- Actionable Insights for Proactive Compliance 42Signals doesn’t just help brands react to violations; it provides actionable insights that enable proactive compliance management. By analyzing data trends, the platform can help brands anticipate potential issues and take preemptive steps to prevent violations from occurring in the first place. For example, if a brand sees increased violations from specific regions or platforms, it can implement additional controls or policies to mitigate the risk.
Challenges and Considerations in MAP Compliance
In a multi-channel retail environment, brands face significant hurdles in ensuring that all retailers, both online and offline, adhere to MAP guidelines. These challenges range from legal complexities to managing customer expectations and keeping retailers aligned with the policy.
Below is a comprehensive look at the common challenges brands face in enforcing MAP policies, strategies for overcoming these barriers, and the delicate balance between enforcing MAP and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Common Challenges in Enforcing MAP Policies
- Complexity of the Multi-Channel Retail Landscape
With the proliferation of online marketplaces, e-commerce websites, and physical stores, maintaining consistent MAP compliance across various channels has become increasingly difficult.
Each channel operates differently, with some—such as Amazon—featuring thousands of third-party sellers who can easily alter prices, often without the brand’s knowledge. Monitoring and enforcing MAP compliance on platforms that facilitate this kind of fragmented sales environment is a major challenge.
- Third-Party Marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Walmart host thousands of independent sellers, making it difficult for brands to keep track of all listings and ensure that MAP policies are being followed. These sellers, who may not be authorized by the brand, often price products below MAP to gain a competitive advantage.
- Cross-Channel Price Discrepancies: With retailers operating across various platforms (their own websites, physical stores, and third-party marketplaces), it’s difficult to maintain uniform pricing. Brands often find that the same product is priced differently across these platforms, undermining MAP policies.
- Unauthorized Sellers and Gray Market Products
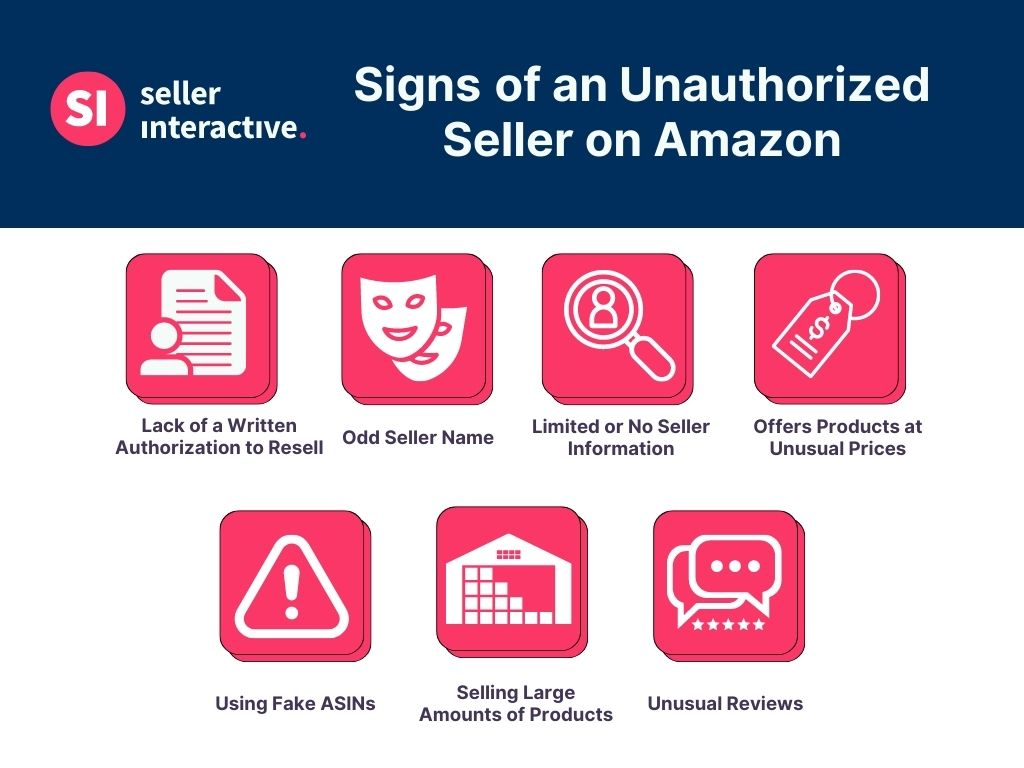
Unauthorized sellers—those who are not part of the brand’s official distribution network—pose a significant threat to MAP enforcement.
These sellers often acquire products through backchannels or overstock liquidation and sell them at a lower price, undercutting authorized retailers and causing brand devaluation.
Gray market products are genuine goods sold through unofficial channels, typically at reduced prices, leading to price erosion and consumer confusion.
- Globalization and Regional Differences
For brands that operate across multiple countries, enforcing MAP policies becomes even more challenging due to varying regulations in different regions. What might be an acceptable MAP enforcement strategy in the U.S. could be considered illegal price fixing in the European Union. Global brands need to account for regional variations in competition laws, consumer protection laws, and price-setting regulations, making consistent enforcement more complex.
- Currency Fluctuations: Prices set in one currency may not align perfectly with another due to fluctuations in exchange rates. This makes it difficult to maintain consistent MAP compliance across international markets.
- Retailer Pushback and Non-Compliance
Retailers often view MAP policies as restrictive and may push back against enforcement. Retailers competing for market share may feel pressured to lower prices to attract customers, even if doing so violates MAP guidelines. This is particularly true for smaller retailers competing with large e-commerce giants that may engage in aggressive pricing strategies.
- Retailer Resistance: Some retailers may argue that MAP policies limit their ability to compete, especially in sectors where price competition is fierce. Brands may face resistance from these partners, leading to strained relationships or, in some cases, retailers opting to stop selling the brand’s products.
- Resource-Intensive Monitoring
Monitoring MAP compliance can be resource-intensive, particularly for large brands with a wide distribution network. Manually tracking pricing across thousands of listings is time-consuming and prone to errors. Even with automated tools, brands still need dedicated teams to manage MAP compliance, respond to violations, and take enforcement actions.
How to Overcome Barriers to MAP Compliance?

Despite the challenges, there are several strategies that brands can adopt to overcome these barriers and ensure that MAP policies are enforced effectively.
A proactive, technology-driven approach combined with strong retailer relationships is key to ensuring long-term MAP compliance.
- Leverage Technology and Automation: Brands can overcome many MAP compliance challenges by investing in robust, automated monitoring tools like 42Signals or other MAP monitoring platforms. These tools scan websites, marketplaces, and other online platforms to identify MAP violations, providing immediate alerts to the brand so that corrective actions can be taken.
- Work Closely with Retail Partners: Strong relationships with retail partners are critical for successful MAP enforcement. Brands should focus on educating retailers about the importance of MAP compliance and how it benefits both the brand and the retailer in maintaining a healthy market. Retailers who understand the long-term benefits of consistent pricing are more likely to comply with MAP policies.
- Address Unauthorized Sellers: Dealing with unauthorized sellers can be difficult, but it’s essential for MAP compliance. Brands should invest in marketplace monitoring tools that identify unauthorized sellers and work with the platform (e.g., Amazon) to remove listings that violate MAP policies.
- Take-Down Requests: For third-party marketplaces like Amazon, brands can file take-down requests for unauthorized listings. Enrolling in Amazon’s Brand Registry program gives brands more control over how their products are listed and allows them to take enforcement actions directly.
Balancing MAP Enforcement with Customer Satisfaction
One of the biggest considerations for brands enforcing MAP policies is how to balance enforcement with maintaining customer satisfaction. Customers, particularly in e-commerce, are highly price-sensitive and may gravitate toward lower-priced options. Striking a balance between enforcing MAP policies and keeping customers happy can be challenging, but it is necessary for long-term success.
- Avoid Overly Restrictive Pricing
While MAP policies are necessary to prevent price erosion, they should not be so restrictive that they drive customers away to cheaper alternatives. Brands need to strike a balance between setting a minimum price that preserves brand value and ensuring that customers still feel they are getting good value for their money.
- Offer Value Beyond Price
Brands should focus on offering customers value beyond just price, particularly in sectors where quality, customer service, or product features are important factors in purchasing decisions. By emphasizing the quality and benefits of the product, brands can shift customer attention away from the price and reduce the impact of price sensitivity.
- Customer Education and Transparency
Educating customers on the importance of consistent pricing and brand value can help mitigate the frustration that comes from MAP enforcement. Brands can use marketing messaging to explain why maintaining consistent pricing benefits the customer, such as ensuring that they receive authentic products and high-quality service from authorized retailers.
- Allow Flexibility for Special Circumstances
Brands should consider allowing flexibility in MAP policies during special sales periods, such as Black Friday, or in cases where competitive pricing strategies are necessary to meet market demands. Creating well-defined exceptions for specific sales events allows retailers to remain competitive while ensuring that MAP policies are generally upheld throughout the rest of the year.
Real-World MAP Compliance: Case Studies & Insights
Many brands have successfully implemented MAP compliance strategies, leading to more stable pricing and healthier retailer relationships.
One notable example is Nike, which has taken a proactive approach to MAP enforcement by leveraging automated price monitoring tools. Through consistent monitoring and retailer education, Nike was able to maintain pricing integrity across multiple channels, reducing violations and improving overall retailer adherence.
Another example is Sony, which experienced success in enforcing MAP policies by issuing clear guidelines to retailers and investing in monitoring tools that provided real-time alerts for violations. As a result, Sony effectively minimized price undercutting on major online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay, protecting its premium brand image.
Examples of Brands Resolving MAP Violations
Apple faced significant challenges with unauthorized sellers on online platforms. By enrolling in Amazon’s Brand Registry and employing advanced MAP enforcement tools, Apple managed to reduce the number of unauthorized listings and price violations.
Through strategic legal actions, including cease-and-desist letters and collaborations with marketplace platforms, Apple restored MAP compliance across its authorized seller network.
Another case involves Patagonia, which handled recurring MAP violations by reinforcing its partnership with compliant retailers. The company incentivized these retailers with exclusive products and marketing support while cutting ties with violators.
This strategy not only resolved MAP issues but also strengthened relationships with key partners.
Lessons Learned from MAP Violation Scandals
Brands like LG and Samsung learned valuable lessons from past MAP violation scandals, where pricing inconsistencies damaged their reputation. In both cases, insufficient enforcement and unclear policies allowed widespread price undercutting.
These brands responded by tightening enforcement, employing more rigorous monitoring, and improving communication with retailers. The key takeaway from these scandals is that lax enforcement and poor communication can lead to brand devaluation, but proactive strategies and transparent policies can help recover from these missteps.
Future of MAP Violations and Compliance
One significant trend is the increased use of AI and machine learning to detect pricing violations more effectively. These technologies are helping brands monitor thousands of listings across global platforms, providing faster and more accurate violation alerts.
Additionally, the rise of omnichannel retailing means that MAP policies must now account for consistency across both online and offline sales, further complicating enforcement.
Key Takeaways
Managing and preventing Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) violations is crucial for preserving a brand’s value, ensuring fair competition, and maintaining strong relationships with retailers.
Key points to remember include:
- Importance of MAP Policies: MAP policies protect brands from price erosion and ensure a level playing field across retail channels. By preventing price undercutting, these policies help preserve brand integrity and maintain profitability for both the brand and its authorized retailers.
- Challenges in Enforcement: The increasing complexity of multi-channel retailing, the presence of unauthorized sellers, and global market differences make enforcing MAP policies difficult. Brands face significant challenges in consistently applying MAP policies, especially on third-party marketplaces like Amazon.
- Tools and Strategies for Compliance: Automated tools like price monitoring software, marketplace monitoring platforms, and legal enforcement services are essential for detecting and addressing MAP violations. Proactively using these eCommerce analytics tools, combined with strong communication and incentivizing retailer compliance, can significantly reduce violations.
- Case Studies and Lessons Learned: Real-world examples from brands like Apple, Sony, and Nike show that rigorous enforcement, clear communication, and consistent policy application lead to successful MAP compliance. Lessons from brands that struggled with MAP violations highlight the importance of proactive monitoring and legal safeguards.
- Future Trends: The use of AI and machine learning is transforming how brands detect MAP violations, while omnichannel retailing adds new complexities to enforcement. As e-commerce grows, brands will need to adapt to evolving regulations and consumer behaviors to stay competitive and compliant.
Conclusion
Preventing and managing MAP violations is a continuous process that requires vigilance, collaboration, and technological support. Brands must take a proactive approach by clearly communicating MAP policies, investing in automated price monitoring solutions, and consistently enforcing these policies across all sales channels.
By doing so, they not only protect their pricing strategy but also reinforce their relationships with retail partners.
To ensure long-term success, brands should focus on fostering trust and transparency with their retail networks, offering incentives for compliance, and utilizing the latest tools and services to stay ahead of potential violations.If you are curious to see how prompt detection of MAP violations can help your brand, schedule a demo with our experts.




