A “House of Brands” is a strategic business model in which a company owns and manages multiple distinct brands, each with its own unique identity, target audience, and market positioning.
Unlike a “Branded House,” where a single brand name is used across all products and services, a House of Brands allows each brand to operate independently, maintaining its individual image and value proposition.
This approach enables the parent company to cater to diverse consumer needs, tap into various market segments, and minimize risks by diversifying its portfolio.
Notable examples of companies employing the House of Brands strategy include Procter & Gamble, Unilever, and Nestlé, which manage numerous brands across different product categories, from household goods and personal care items to food and beverages.

Image Source: Brigade
Managing a House of Brands
Managing multiple brands under one roof, a house of brands, is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor. It demands a strategic approach to ensure that each brand thrives without cannibalizing the others. Here are some key strategies to help you manage multiple brands effectively:
1. Develop a Clear Brand Architecture
A well-defined brand architecture is crucial for managing multiple brands. There are three primary types of brand architecture:
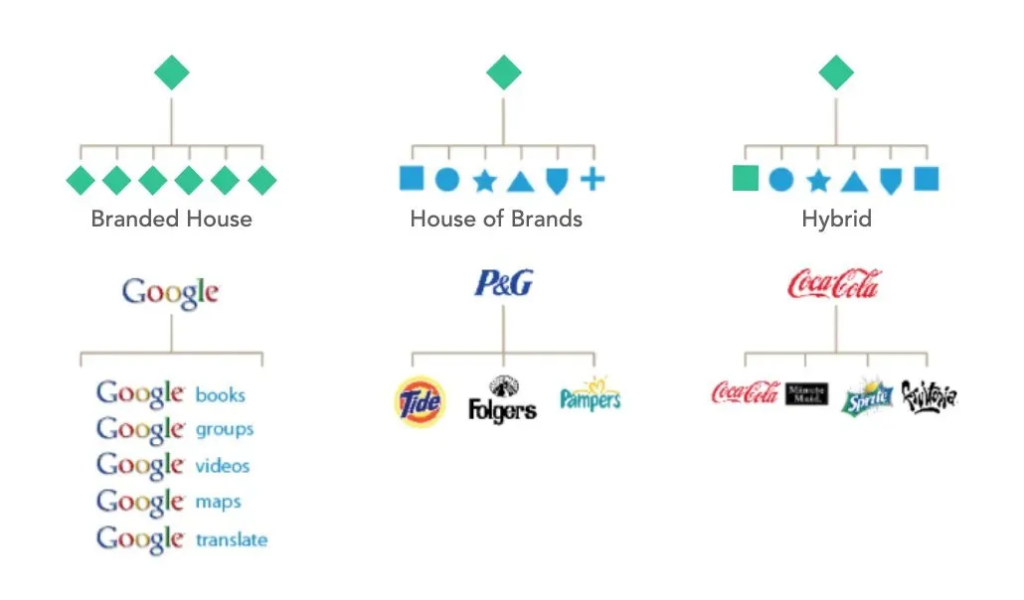
House of Brands: Each brand operates independently with its own unique identity. This approach allows for diverse positioning but requires significant resources to manage each brand individually.
Branded House: The master brand dominates and extends its influence across all sub-brands. This approach leverages the strength of the master brand but may limit the distinctiveness of individual brands.
Hybrid Model: A combination of both, where some brands operate independently while others are closely linked to the master brand. This model offers flexibility but requires careful management to avoid confusion.
Choosing the right architecture depends on your business goals, target markets, and brand equity. A clear structure helps streamline marketing efforts and resource allocation.
2. Maintain Consistent Brand Values
While each brand may have its unique identity, maintaining consistent core values across all businesses under the house of brands is vital.
Consistent values build trust and credibility with consumers. Ensure that each brand’s messaging aligns with the overarching company values.
For example, if sustainability is a core value, every brand under your umbrella should reflect this in their practices and communications. This consistency reinforces your commitment to your values and helps build a cohesive brand portfolio.
3. Centralize Administrative Functions
While brand identities should be distinct, administrative functions can be centralized to achieve economies of scale and improve efficiency.
Functions such as HR, finance, IT, and procurement can be shared across businesses, reducing redundancy and operational costs.
Practical Steps:
- Shared Services Model: Implement a shared services model for administrative functions, allowing each brand to focus on its core activities while benefiting from centralized support.
- Standardized Processes: Develop standardized processes and systems for administrative tasks to ensure consistency and efficiency across brands.
- Integrated Technology: Utilize integrated technology solutions to streamline operations and enhance communication between brands and centralized functions.
4. Strategic Brand Positioning

Image Source: Enigma
Strategic brand positioning involves understanding and optimizing the market positions of each brand to avoid cannibalization and maximize market share.
This requires thorough market research, competitive analysis, and strategic planning.
Practical Steps:
- Market Segmentation: Segment the market accurately and position each brand to target specific customer segments without overlapping.
- Competitive Analysis: Conduct regular competitive analysis to understand the market landscape and adjust brand positioning strategies accordingly.
- Portfolio Management: Use portfolio management techniques to assess the performance of each brand and make strategic decisions about investment, development, or divestment.
5. Effective House of Brands Communication Strategies
Tailoring communication strategies to suit the unique identity and target audience of each brand is essential.
However, these strategies should also align with the overarching corporate goals and values.
Practical Steps:
- Customized Marketing Campaigns: Develop customized marketing campaigns for each brand, considering their unique identities and customer bases.
- Consistent Messaging: Ensure that the messaging across all brands is consistent with the company’s core values and strategic objectives.
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC): Implement an IMC approach to create a seamless experience for customers, ensuring that all communication channels work together effectively.
6. Leverage Data and Analytics
Data and analytics play a crucial role in managing a house of brands effectively. By leveraging data, companies can gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and brand performance, enabling informed decision-making.
Practical Steps:
- Customer Insights: Use data analytics to gather insights into customer preferences and behavior for each brand, tailoring marketing and product strategies accordingly.
- Performance Metrics: Establish key performance metrics for each brand and use data analytics to monitor and evaluate performance.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilize predictive analytics to anticipate market trends and customer needs, allowing proactive strategy adjustments.
7. Adaptability and Continuous Improvement
In a dynamic market, adaptability and continuous improvement are essential for sustaining the success of a house of brands. This involves staying abreast of market trends, being responsive to customer feedback, and continuously refining strategies.
Practical Steps:
- Market Monitoring: Regularly monitor market trends and competitor activities to identify opportunities and threats.
- Customer Feedback: Actively seek and act on customer feedback to improve products, services, and customer experiences.
- Continuous Learning: Foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement, encouraging employees to stay updated with industry developments and enhance their skills.
8. Effective Leadership and Governance

Image Source: Brand Marketing Blog
Strong leadership and governance are critical for the successful management of multiple verticals under the house of brands. Leaders must be adept at balancing the strategic objectives of the company with the individual needs of each brand.
Practical Steps:
- Leadership Development: Invest in leadership development programs to cultivate leaders who can effectively manage multiple brands and drive overall company success.
- Governance Structures: Establish robust governance structures that provide oversight and strategic direction for all brands while allowing flexibility and autonomy.
- Transparent Decision-making: Ensure transparent decision-making processes that consider the perspectives and interests of all brands.
Conclusion on House of Brands
Managing multiple brands under one roof is a complex but rewarding endeavor. A house of brands model offers significant advantages in terms of brand specialization and market reach but also presents challenges in terms of brand management and resource allocation.
It’s not for every business, but if done right can prove to be a lucrative business.
If you liked this article, visit our insights and blog page.




