What is MAP Pricing?
MAP pricing, or Minimum Advertised Price, is a pricing policy that sets the lowest price that a retailer can advertise a product for sale. This policy is usually set by the manufacturer or distributor and applies to all retailers that sell the product.
Following pricing best practices is important because it helps to maintain a level playing field among retailers, prevent price wars, and preserve the value of a product.
For eg., Let’s consider a fictional brand of smartphones called “TechWiz” that implements a MAP policy. The MAP for their latest model is set at $500. Now, imagine a retail store called “Tech Store” that sells these smartphones.
According to the MAP policy, Tech Store cannot advertise or display the latest TechWiz model for a price lower than $500 in their marketing materials, both online and in-store. So, if Tech Store wants to promote the TechWiz model, it can mention its features, benefits, and availability on its website or in its physical store, but it cannot display or advertise a price lower than the MAP of $500.
Tech Store can sell the TechWiz model for $550, $600, or any higher price, but they cannot publicly advertise or display the price as $499 or any amount below the MAP.
By setting a minimum price that all retailers must adhere to, manufacturers can protect their brand’s reputation and prevent retailers from competing solely on price, which can lead to a race to the bottom.
MAP prices also help to ensure that retailers can make a reasonable profit while still providing consumers with a fair price. Enforcing MAP policies helps to maintain a healthy market for both manufacturers and retailers while providing consumers with consistent and fair pricing. There are various pricing best practices involved.
Creating a MAP Policy and Communicating with Retailers
Creating a clear and concise MAP policy is an important step in enforcing MAP policy. The policy should clearly outline the minimum advertised price (MAP) for each product, the consequences for violating the policy, and any exceptions to the policy. There are many pricing best practices involved.
Once the policy has been created, it’s important to communicate it clearly with retailers. This may involve sending a copy of the policy to retailers and discussing it with them in person or over the phone. It’s also important to build strong relationships with retailers and establish open lines of communication.
Regularly checking in with retailers and addressing any concerns they may have can help to prevent misunderstandings and limit the potential for violations. By creating a clear and well-communicated MAP policy, manufacturers can help to ensure that retailers understand the rules and consequences of violating the policy, and encourage compliance with the policy.
Common Challenges in Enforcing MAP Pricing
Enforcing MAP policies can be challenging for manufacturers and distributors. Below are a few of the challenges they may face:
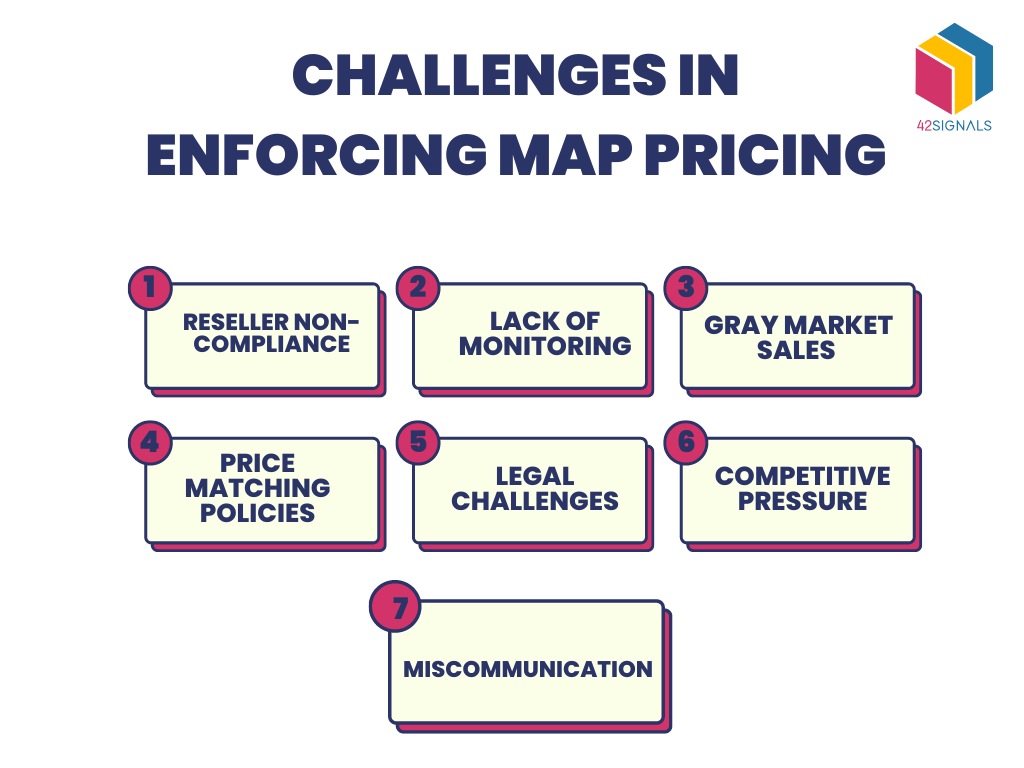
• Reseller non-compliance
Retailers may choose not to adhere to MAP pricing policies in order to gain a competitive advantage or increase sales.
• Lack of monitoring
Without proper monitoring and enforcement measures, manufacturers may not be aware of MAP violations or be able to take action in a timely manner.
• Gray market sales
Products may be sold through unauthorized channels, making it difficult to monitor and enforce MAP pricing.
• Price matching policies
Retailers may use price matching policies to undercut MAP pricing, making it difficult to maintain consistent pricing across all channels.
• Legal challenges
Some retailers may challenge the legality of MAP pricing policies, leading to legal battles and uncertainty around enforcement.
• Competitive pressure
Manufacturers may face pressure to lower MAP pricing from competitors who are not adhering to MAP pricing policies.
• Miscommunication
Lack of clear communication or understanding of MAP pricing policies between manufacturers and retailers can lead to confusion and violations.
Best Practices
To effectively monitor and enforce MAP, manufacturers and distributors can follow these best practices:
Image Source: Valido
1. Use automated monitoring tools
Utilize automated tools to scan retailer websites and online marketplaces for pricing below the minimum advertised price (MAP).
2. Review pricing data regularly
Stay updated on market trends and pricing behavior by regularly reviewing pricing data.
3. Communicate with retailers
Maintain strong relationships with retailers and communicate regularly to identify potential violations and resolve issues.
4. Provide clear policies
Ensure MAP policies are clear and concise to avoid misunderstandings and minimize violations.
5. Enforce consistently
Treat all retailers equally and enforce MAP consistently. This helps to avoid any perception of bias or favoritism.
6. Stay informed about legal regulations
Stay up to date with legal regulations concerning minimum advertised policies to avoid legal issues and ensure policy compliance.
7. Respond promptly to violations
Respond to MAP policy violations promptly and consistently. A timely response shows that the policy is taken seriously and reinforces the importance of adhering to it.
8. Consider incentives
Offer incentives to retailers that comply with MAP pricing policies, such as exclusive product access or promotional materials.
9. Have strategies in place to deal with MAP violations
Establish proactive measures like warnings, penalties, and progressive discipline for repeat offenders. A clear plan of action enables consistent and efficient responses to violations, ensuring the integrity of the MAP policy.
Strategies for Dealing with MAP Pricing Violations
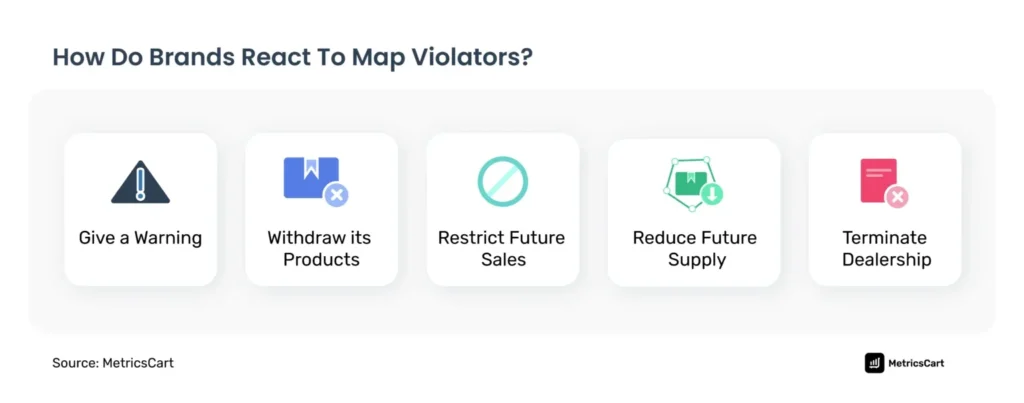
Image Source: Metrics Cart
Here are some strategies for dealing with MAP pricing violations:
Contact the retailer
The first step in dealing with a MAP violation is to contact the retailer directly. Manufacturers should provide clear evidence of the violation and request that the retailer adjust the price to comply with the policy.
Issue a warning
If the violation persists, manufacturers may issue a warning to the retailer, outlining the consequences of continued violations. This can include loss of authorized dealer status or other sanctions.
Enforce consequences
If warnings are ignored, manufacturers may need to enforce consequences for continued MAP violations. This can include terminating contracts or reducing the supply of products to the retailer.
Take legal action
In some cases, manufacturers may need to take legal action to enforce MAP pricing policies. This can include filing a lawsuit or working with regulatory agencies to investigate and enforce the policy.
Consider the bigger picture
It’s important for manufacturers to consider the bigger picture when dealing with MAP violations. This includes considering the potential impact on their brand reputation, their relationships with other retailers, and the overall market for their products
Maintain consistency
Consistency is key when dealing with violations. Manufacturers should ensure that all retailers are held to the same standards and that violations are addressed in a timely and consistent manner.
Review and adjust policies
Manufacturers should regularly review and adjust their MAP policies as needed to ensure that they are effective and aligned with market trends and legal regulations. This can help to prevent future violations and ensure that the policy remains relevant over time.
Conclusion
Enforcing MAP policies can bring several benefits to manufacturers, such as:
Protecting brand value
Enforcing MAP pricing can help manufacturers protect the value of their brands and products. By preventing retailers from undercutting each other on price, manufacturers can maintain a consistent brand image and prevent price erosion.
Promoting healthy competition
Enforcing MAP can create a level playing field among retailers, promoting healthy competition and ensuring that retailers compete on factors other than price.
Boosting profitability
By ensuring that all retailers sell products at a consistent price, manufacturers can maintain higher profit margins and avoid price wars that can ultimately hurt profitability.
Building stronger relationships with retailers
Enforcing MAP pricing can help manufacturers build stronger relationships with retailers by demonstrating that they are committed to maintaining fair and consistent pricing policies.
Next steps for manufacturers looking to enforce MAP policies may include regularly monitoring compliance with the policy, addressing violations quickly and consistently, and adjusting the policy as needed to stay up to date with market trends and changes in pricing behavior.
It’s also important to regularly communicate with retailers to ensure that they understand the policy and the consequences of violating it. By taking a proactive approach to enforcing MAP pricing best practices, manufacturers can protect their brand value, promote healthy competition, and boost profitability.




