Imagine navigating the dynamic landscape of e-commerce, where upholding the integrity of a brand is a top priority. Enter Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies – a strategic tool employed by manufacturers. These policies establish the minimum prices at which resellers can showcase their products. It’s essentially a collaborative pact between suppliers and retailers, strategically crafted to prevent any pricing conflicts. By doing so, it becomes a shield, preserving the brand’s reputation and ensuring a harmonious market presence preventing MAP violations.
The significance of this policy lies in its ability to uphold a product’s perceived value, foster fair competition for smaller retailers, and ensure robust profit margins across diverse sales channels. With the continued expansion of e-commerce, the effective enforcement of MAP policies emerges as a critical element for securing enduring brand success.
What is a MAP Violation?
If a retailer advertises a product on their digital shelf for a price lower than what the manufacturer suggests, it’s called a Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) violation. Manufacturers have MAP policies to maintain the brand image and help retailers maintain their profits. It’s like a rulebook to make sure everyone plays fair and the brand keeps its value. Violations typically happen when:
- Retailers inadvertently overlook policy details
- Intentional undercutting in competitive markets
- E-commerce platforms automate pricing, leading to accidental breaches
MAP pricing violations strain manufacturer-retailer relationships, risking brand image and consumer perception. Monitoring and strict enforcement of the MAP Policy are crucial to swiftly address and prevent these issues, maintaining a positive brand image and supply chain harmony.
Impacts on Brand Integrity and Consumer Trust
When Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies are violated, they can trigger various negative consequences, such as:
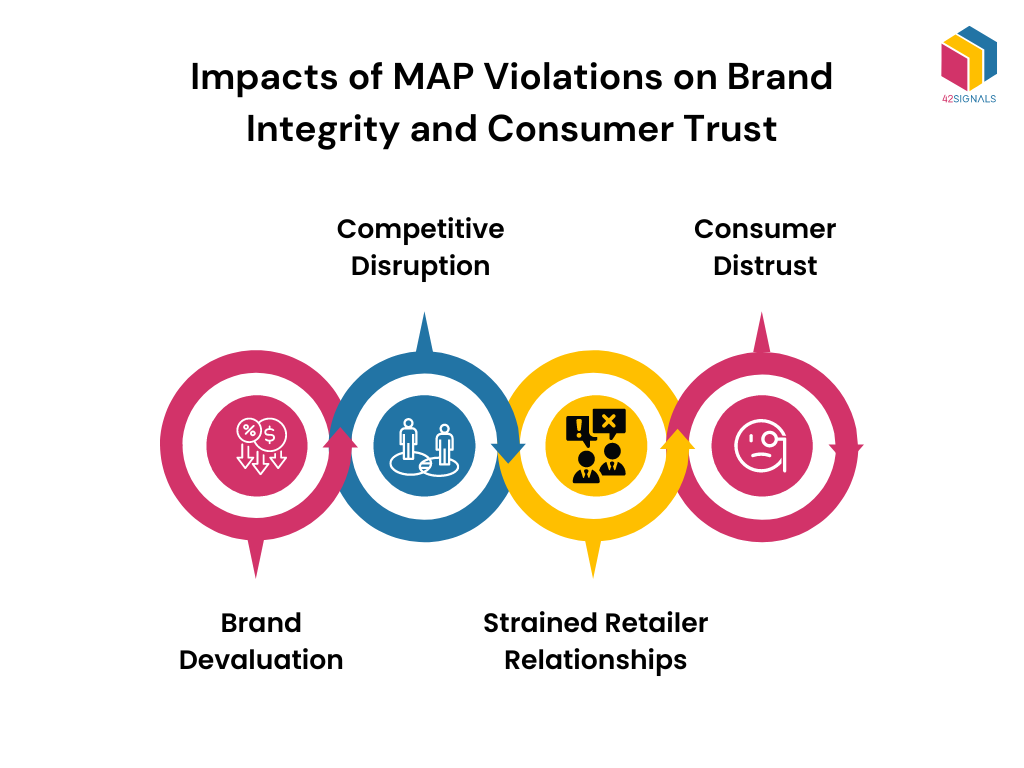
- Brand Devaluation: Constantly finding products available at lower prices can make consumers perceive them as lower in quality or less prestigious, diminishing the brand’s perceived value.
- Competitive Disruption: MAP violations can spark a price war, forcing other sellers to lower their prices to compete, potentially degrading the market value of the product.
- Retailer Relationships: Consistent MAP pricing violations strain relationships between brands and honest retailers, who may feel compelled to break MAP policies or drop the brand from their inventory due to unfair competition.
- Consumer Distrust: When consumers notice price discrepancies, they may suspect product authenticity or doubt the legitimacy of the retailer, ultimately leading to mistrust towards the brand.
A brand’s reputation can suffer significant damage from MAP violations, demonstrating the importance of enforcing these policies for long-term brand health and consumer confidence.
What is MAP Compliance?
Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) Compliance refers to retailers adhering to manufacturers’ set pricing standards for advertising products, which the retailers commit to this price floor when choosing to stock a brand’s items.
Violation of these policies may result in warnings, penalties, or even losing the privilege to sell certain brands, negatively impacting retailer-supplier relationships. Complying with MAP policies is vital for maintaining a brand’s perceived value and ensuring stability in the market.
Legal Aspects of MAP Enforcement in Online Retail
Ensuring the enforcement of Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies in online retail relies on legal frameworks rooted in antitrust laws and agreements between manufacturers and retailers. Retailers frequently engage in contracts with manufacturers, committing to follow MAP policies to steer clear of legal consequences. Manufacturers might:
- Monitor online pricing to ensure compliance
- Issue warnings to retailers for MAP pricing violations
- Enforce penalties, such as ceasing supply or removing from an authorized retailer list

Image Souce: Metricscart
Nonetheless, enforcing MAP agreements poses challenges as retailers can sometimes leverage various legal arguments centered on anti-competitive practices. Moreover, the rise of third-party marketplaces further complicates the enforcement landscape. Understanding the legal nuances and proper documentation is vital for effective MAP policy application and preservation of brand value.
What is MAP Violation policy?
MAP policy, serves as a manufacturer or brand’s set guideline for the lowest price at which a product can be advertised. Retailers opting to carry these products commit to following the MAP, ensuring a uniform brand image and price perception for consumers.
While the policy doesn’t dictate the sale price, it monitors the advertised price, safeguarding brand value and maintaining dealer margins.
Strategies for Monitoring MAP Pricing Violations
- Employing Automated Monitoring Tools: Leveraging software solutions can scan multiple online retailers simultaneously, alerting brands to potential MAP violations.
- Establishing a Dedicated Team: Some companies allocate resources to a team focused on tracking and enforcing MAP policies across various e-commerce platforms.
- Partnering with Online Marketplaces: Collaboration with platforms like Amazon or eBay can highlight unauthorized sellers or listings that undercut MAP.
- Regular Mystery Shopping: Conducting undercover purchases can help identify retailers not adhering to MAP, along with the quality of the product being sold.
- Vendor Agreements and Audits: Implementing robust agreements with distributors or retailers and periodic audits ensures MAP compliance and traceability.
Best Practices to Address Price Violations
- Develop a comprehensive MAP policy: Clearly outline expectations and consequences for non-compliance.
- Educate your resellers: Ensure all partners understand the MAP policy fully.
- Monitor the market: Use automated tools to track pricing across platforms.
- Enforce consistently: Address violations immediately and uniformly to maintain policy integrity.
- Build strong relationships: Engage with resellers to create mutual understanding and respect for pricing policies.
- Stay legally compliant: Ensure your MAP policy is enforceable under current antitrust laws.
The Role of Technology in MAP Enforcement
Technology plays a critical function in enforcing Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies and ensuring compliance. Advanced software solutions proactively monitor online retailers, marketplaces, and other digital platforms to identify MAP pricing violations quickly. These automated systems can:
- Scan numerous product listings across various e-commerce channels for price discrepancies
- Utilize data analysis to track pricing patterns and potential breaches
- Send instant alerts when price violations are detected
- Provide comprehensive reporting tools for brands to assess the extent of non-compliance
- Automate communications with violators for efficient resolution.
Utilizing these technological resources allows brands to preserve their integrity and maintain fair market value with minimal manual oversight.
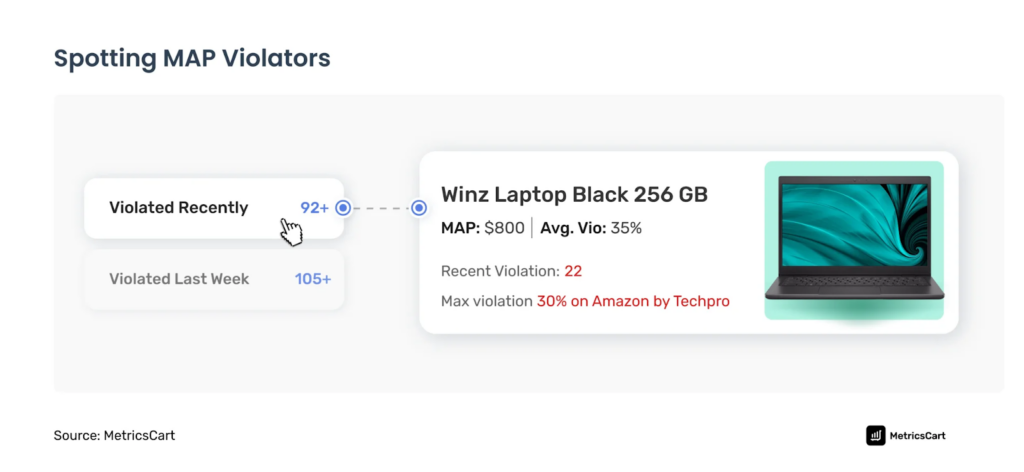
Image Source: Metricscart
Conclusion
Advancements in technology and analytics are set to revolutionize the tracking and enforcement of Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) compliance. Expect brands to opt for cutting-edge software solutions, enabling swift monitoring and reporting of violations.
Collaboration between e-commerce platforms and manufacturers may become more systemic to maintain brand integrity. Furthermore, with the increase in online shopping, regulatory bodies might step up efforts to establish standardized MAP enforcement practices across digital marketplaces, aiming to protect both consumers and businesses.
42Signals helps brands detect price violations and take the right actions to combat them. Sign up for a free trial today.