Pricing is the primary criterion for 60% of consumers when making a purchase decision, according to a study by Prisync, making it a critical factor for brands to determine e-commerce pricing strategies. Price elasticity in ecommerce is a crucial concept that analyzes the extent of demand for a product and how it varies during price fluctuations. It measures the degree of responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a product to changes in its prices.
For instance, a brand that raises the prices of its products is likely to experience a decrease in sales compared to when the same products are sold at lower prices.
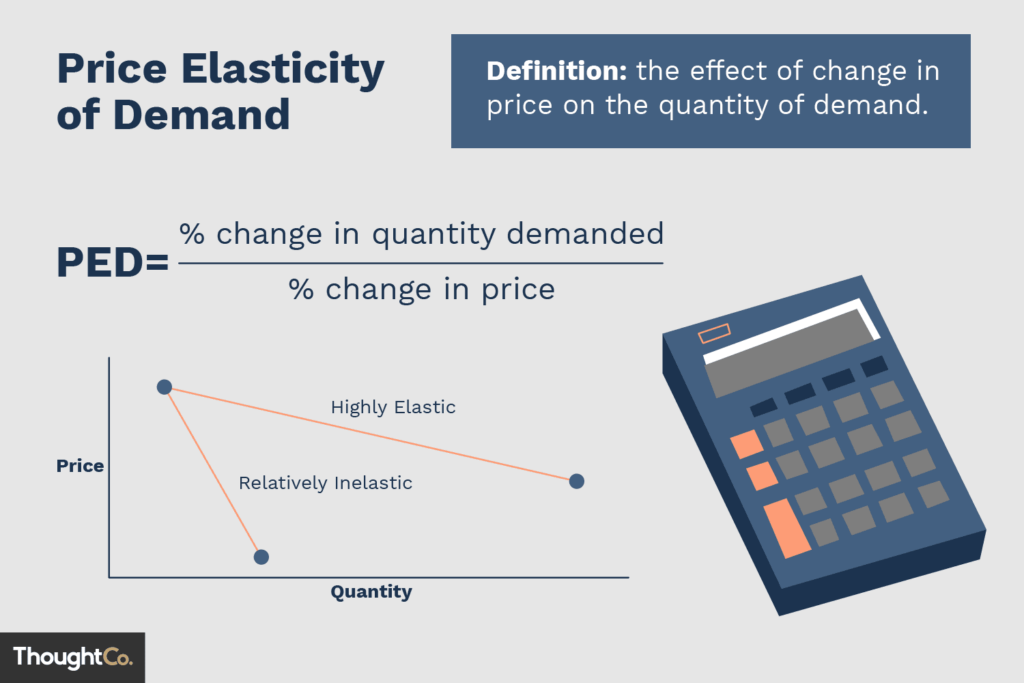
Image Source: Thought Co
Price elasticity is not just about acknowledging the fact that a lower price will attract more buyers, but it involves a deeper analysis of the number of buyers who will purchase the product at a lower price compared to the number of buyers who will still buy the product even if the price increases.
It helps businesses to determine the optimal price at which they can maximize their revenue and profit.
Given that 90% of shoppers spend time searching for the best online price for a product, it’s crucial for e-commerce brands to establish competitive pricing that meets consumer expectations.
Let’s take a deeper dive into price elasticity in ecommerce and ways brands can determine optimal pricing.
Why Should You Care about Price Elasticity?
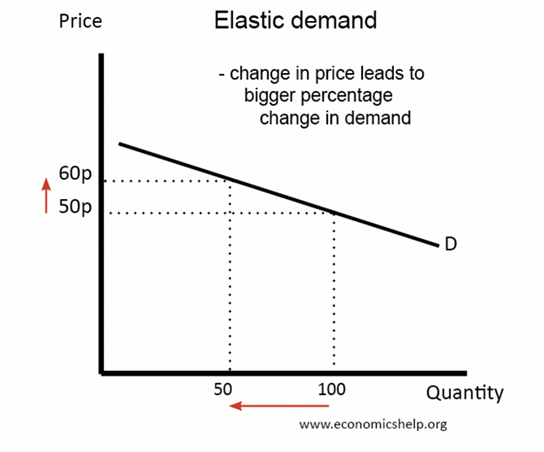
Source: Economicshelp.org
Consider the graph above as an example. At a price of 50 pence, the product sold 100 pieces. However, when the price was increased to 60 pence, the demand for the same product dropped significantly, with only 50 pieces sold.
Despite the price difference of only 10 pence, the demand for the product was drastically altered, resulting in a 50% decrease in sales. This illustrates the importance of understanding price elasticity in ecommerce and determining the optimal pricing strategy for your products.
Price elasticity is calculated by –

Image Source: Investing Answers
The concept of price elasticity is determined by the percentage change in quantity demanded of a product in response to a change in its price. This measurement can be used to determine whether a product has high elasticity, also known as elastic demand, or low elasticity, known as inelastic demand.
A product with high elasticity or elastic demand experiences a significant change in the quantity demanded in response to a small fluctuation in price. On the other hand, a product with low elasticity or inelastic demand experiences little to no change in the quantity demanded in response to a fluctuation in price, meaning that the change in price has no effect on the product demand.
Electricity, water, medicines, and even gasoline are good examples of inelastic demand. People continue to purchase them even when prices fluctuate as usually there’s no substitute for these items and they are necessary purchases. On the other hand, luxury goods, electronics, clothing, and cars are very elastic and can be classified as products with elastic demand.
They are not necessities, and any fluctuations in prices will have a direct impact on the quantity demanded. Items in these categories typically have substitutes so if the product’s price increases, consumers can opt for a similar item from a different brand.
Finding out where your product lies on the scale of elasticity can help determine e-commerce pricing strategies and find the optimal price point. With the above formula, product values close to 0 are inelastic and those far from zero are elastic. To calculate the price elasticity for your product, there are several methods that you can use, the formula listed above is a good starting point.
HubSpot has a useful article that guides you through the process of calculating price elasticity. It is important to note that this calculation is not a one-time event and needs to be continuously monitored and adjusted based on market trends and consumer behavior.
Determining Optimal Pricing
Image Source: Analyst Prep
There are a few factors that determine the price elasticity of a product. The availability of substitutes or alternatives is one factor, the degree of necessity is another, and even the proportion of a person’s income spent on an item can determine where the product falls on the elasticity scale.
Ideally, there are a few steps to find out how to price products –
- Conduct Market Research: To set your product’s optimal pricing, conducting comprehensive market research is the first place to start. It involves analyzing other products in the same segment to identify the price range that your product can fit into. Additionally, conducting surveys and focus groups to collect product feedback can provide valuable insights into how much customers are willing to pay for your product.
- Analyze Pricing Model: To establish optimal pricing, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your product’s production costs. This not only includes the cost of raw materials, but also shipping, packaging, warehouse storage, and marketing expenses. With this data in hand, you can set a minimum price point that ensures profitability.
- Monitor Competitors: Although researching competitors’ pricing strategies is a part of market research, it can be equally necessary for achieving success. By analyzing their pricing models and promotions, brands can identify opportunities to differentiate their pricing strategy to attract more customers. E-commerce analytics tools like 42Signals can help brands track competitors’ pricing changes, such as when they put items on sale or fluctuating prices. Competitor price monitoring can be used to make informed pricing decisions and stay competitive in the market.
- Test Prices: A/B testing is an effective way to measure price elasticity and determine how customers respond to different price points. To conduct this experiment, an existing customer base can be divided into groups, and each group can be exposed to a different price point. By measuring the results, businesses can identify the optimal price point that maximizes profits while still maintaining customer satisfaction.
- Employ Dynamic Pricing: Dynamic pricing is a strategy that involves adjusting prices based on various factors such as demand, supply, market data, competitor pricing, and product inventory levels. This approach is based on the fundamental principle of business that suggests increasing prices when demand is high and lowering them when it’s low. By doing so, brands can create patterns in consumer behavior and use these insights to refine their pricing strategies.
To learn more about effectively pricing your products, we highly recommend reading our comprehensive pricing guide that provides strategies and tips for pricing competitively in today’s market.
Conclusion
Price elasticity in ecommerce is a crucial aspect that can lead to success when approached thoughtfully. It’s an ongoing process that relies on constant feedback and research to determine optimal pricing points. External factors such as shifting consumer behavior, new product releases, and market conditions can all impact a product’s price elasticity, whether it falls under elastic or inelastic demand.
Keeping up with sound market data is essential to building effective e-commerce pricing strategies. This is where 42Signals, an AI-powered solution suite for consumer brands, comes in. It enables brands to anticipate consumer demand, track competition, optimize digital shelves, and grow online sales. By leveraging this data, you can ensure that your pricing strategy remains competitive and relevant in a dynamic market.







