To operate as a global business, understanding and optimizing the supply chain is more crucial than ever. This is where Supply Chain Analytics (SCA) comes into play, offering a powerful combination of data analysis and business intelligence to revolutionize how supply chains are managed.
Global conglomerates like McDonald’s and KFC, Adidas and Nike, Apple and Samsung, became a worldwide success due to their ability to source, manage and optimize their supply chains.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of SCA and how it’s transforming the industry.
Understanding Supply Chain Analytics
At its core, SCA refers to the use of data-driven tools and analysis to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of supply chain processes. This field encompasses a range of analytical approaches and technologies, from basic descriptive analytics to advanced predictive and prescriptive analytics. By analyzing data from various stages of the supply chain – including procurement, manufacturing, distribution, and retail – businesses can gain insights into their operations, predict future trends, and make informed decisions.
Types of Supply Chain Analytics
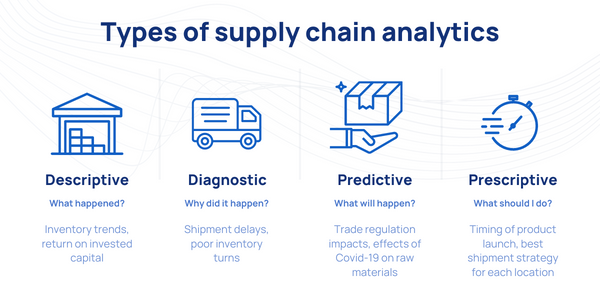
Image Source: SharpCloud
1. Descriptive Analytics
This involves analyzing historical data to understand what has happened in the supply chain in the past.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
It goes a step further by examining data to understand why certain events occurred.
3. Predictive Analytics
This uses statistical models and forecast techniques to predict future events and trends in the supply chain.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
The most advanced form, it suggests a course of action and shows the likely outcome of each decision.
Why is SCA Important?
Enhanced Decision Making
One of the primary benefits of SCA is its ability to enhance decision-making. By providing a clear view of the supply chain, it enables managers to identify inefficiencies, predict potential disruptions, and respond proactively.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
SCA allows companies to better predict customer demand, leading to more effective inventory management. This results in timely deliveries and higher customer satisfaction.
Cost Reduction
By optimizing various supply chain components such as transportation, warehousing, and inventory levels, companies can significantly reduce costs.
Risk Management
SCA helps in identifying potential risks in the supply chain, enabling businesses to devise strategies to mitigate these risks.
Applications of SCA
Demand Forecasting
Predicting future customer demand to optimize inventory levels.
Supplier Performance Analysis
Evaluating suppliers to ensure reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Transportation and Logistics Optimization
Using analytics to find the most efficient routes and modes of transportation.
Sustainability Analytics
Analyzing supply chain practices for environmental impact and sustainability.

Image Source: TowardsAnalytics
The Future of Supply Chain Analytics
The future of SCA is closely tied with advancements in technology. With the rise of AI and machine learning, the capabilities of SCA are rapidly expanding. The integration of IoT devices in the supply chain also offers real-time data collection and analysis, further enhancing decision-making processes.
Conclusion
Supply Chain analytics is not just a trend; it’s a critical component in the modern business landscape. As we continue to advance in the realms of data science and AI, SCA will become even more sophisticated, offering unprecedented insights and efficiency in supply chain management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Examples of Supply Chain Analytics
Demand Forecasting:
Using historical sales data and external factors like seasonality, holidays, and weather to predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
Inventory Optimization
Analyzing inventory levels, lead times, and demand variability to determine the optimal inventory mix and minimize stockouts or overstocking.
Supply Chain Network Design
Evaluating the efficiency of a supply chain network, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing transportation routes to reduce costs and improve delivery times.
Vendor Performance Management
Monitoring supplier performance, tracking KPIs like on-time delivery and quality rates, and working with underperforming suppliers to improve their performance.
Transportation Planning and Execution
Optimizing freight allocation, routing, and scheduling to reduce transportation costs and improve delivery times.
Warehouse Management
Analyzing warehouse operations, optimizing storage space, and streamlining order fulfillment processes to increase efficiency and accuracy.
Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP)
Facilitating collaboration between sales, production, and procurement teams to develop a single integrated plan that aligns demand and supply across the organization.







